Modal phrases or semi modals are used to express the same things as modals but are a combination of auxiliary verbs and the preposition to. All modal auxiliary verbs are followed by a main verb in its base form ; they can never be followed by other modal verbs, lone auxiliary verbs, or nouns. Like other auxiliary verbs, modal verbs work together with a main verb to give a different meaning to a sentence/clause than if the main verb was used by itself. Modal verbs are so common that most English speakers don't even know what the grammatical name for them is. Note that modal auxiliary verbs are a type of auxiliary verb.
Auxiliary verbs encompass tenses, aspects, modality , voice, emphasis and so on. There are many other category of verbs in English like phrasal verbs. In this ESL skills course you can learn natural English phrases. Learn even more about English grammar in this introduction to grammar course. Modal auxiliary verbs are used to uniquely shift the meaning of the main verb they modify, expressing things such as possibility, likelihood, ability, permission, obligation, or intention.
As we will see, how and when we use modal verbs greatly affects the meaning of our writing and speech. Modal auxiliary verbs are used to show a necessity, capability, willingness, or possibility. Unlike most verbs, there is only one form of these verbs.
Typically, verb forms change to indicate whether the sentence's structure is singular or plural. Most verbs also indicate whether something happened in the past, present, or future. This is not the case with most modal auxiliary verbs, which makes them simpler to understand and use correctly. Modal auxiliary verbs combine with other verbs to express ideas such as necessity, possibility, intention, and ability.
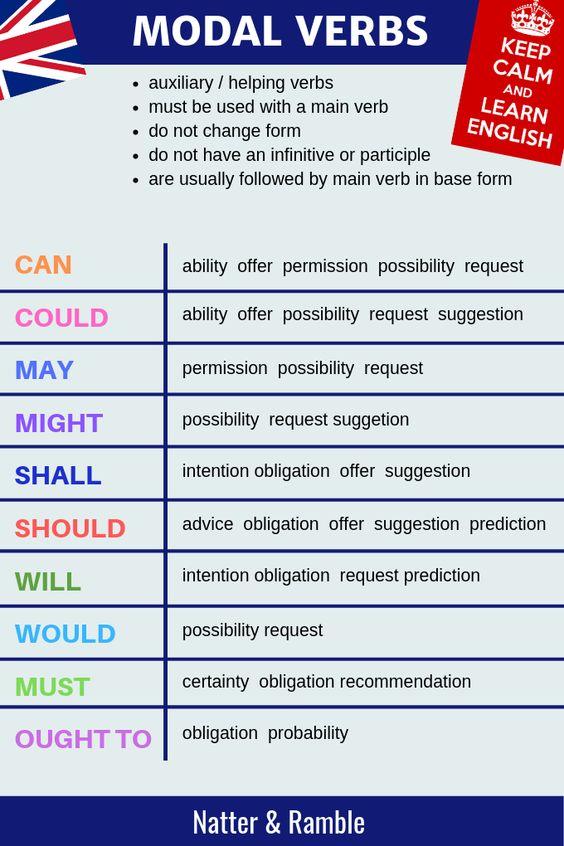
In each example below, the verb phrase is in bold and the modal auxiliary verb is highlighted. As a modal auxiliary verb, will is particularly versatile, having several different functions and meanings. Permission supposition with doubt if not prohibition. The modal verbs of english are a small class of auxiliary verbs used to express possibility obligation advice permission ability.
The modal auxiliary verb would has a variety of functions and uses. It is used in place of will for things that happened or began in the past, and, like shall, it is sometimes used in place of will to create more formal or polite sentences. It is also used to express requests and preferences, to describe hypothetical situations, and to politely offer or ask for advice or an opinion.
Remember that modal verbs are auxiliary verbs, or helping verbs, that are most commonly used to talk about possibility or necessity. You can also use modal verbs to ask for and give permission, describe ability, and give advice. See the section on Conditional Verb Forms for help with the modal auxiliary would.
The shades of meaning among modal auxiliaries are multifarious and complex. Most English-as-a-Second-Language textbooks will contain at least one chapter on their usage. For more advanced students, A University Grammar of English, by Randolph Quirk and Sidney Greenbaum, contains an excellent, extensive analysis of modal auxiliaries. When used with the main verb, modal verbs do not end with -s for the third-person singular. Modal auxiliary verbs never change form, but they have a different form for past tense.
Modal verbs are followed by a base verb the plain dictionary definition of a verb like jump help sing play or read. Learn the list of modal verbs in english with grammar rules and example sentences. I'd wager you use auxiliary verbs and modal auxiliary verbs without giving them a second thought, so I'm mindful that this page has covered a lot of gumpf that you don't really need. Well, that's true provided we're talking about working in English.
If you start learning a foreign language, it won't be too long before you'll be unpicking how they express tense, voice and mood. And, do you know what's a good starting point for that? Modal verbs perform various functions, depending on how they are used within a given text. They show possibilities, abilities, and predictions.
They aid writers in discussing the future with certainty, or discussing the past with uncertainty. They help writers make promises and decisions, as well as give permission or reassurance. Modal verbs also aid other verbs in expressing their meanings. Grammatically, modal verbs make sentences more complete and meaningful.
Modal verbs are auxiliary verbs, also known as helping verbs. They work with other verbs to show various conditions, such as possibility or necessity. Modal verbs do not change form based on the verb tense of the sentence; they do not have conjugated forms. In English, the modal verbs are used to express ability, possibility, permission or obligation. Each one of the modal verbs can be used to express one or more of these modalities. They can also be used to form the future tense in English and to make conditional sentences.
Similarly, we cannot use modal verbs with main verbs that are in a past-tense form; the verb that follows a modal must always be in its base form . Instead, we either use certain modal verbs that have past-tense meanings of their own, or auxiliary have to create a construction that has a specific past-tense meaning. In English, modal verbsare a small class of auxiliary verbs used to express ability, permission, obligation, prohibition, probability, possibility, advice. In many Germanic languages, the modal verbs may be used in more functions than in English. In German, for instance, modals can occur as non-finite verbs, which means they can be subordinate to other verbs in verb catenae; they need not appear as the clause root. In Swedish, some modal verbs have infinitive forms.
This for instance enables catenae containing several modal auxiliaries. The modal verbs are underlined in the following table. In English, main verbs but not modal verbs always require the auxiliary verb do to form negations and questions, and do can be used with main verbs to form emphatic affirmative statements. In the strict sense, though, these other verbs do not qualify as modal verbs in English because they do not allow subject-auxiliary inversion, nor do they allow negation with not.
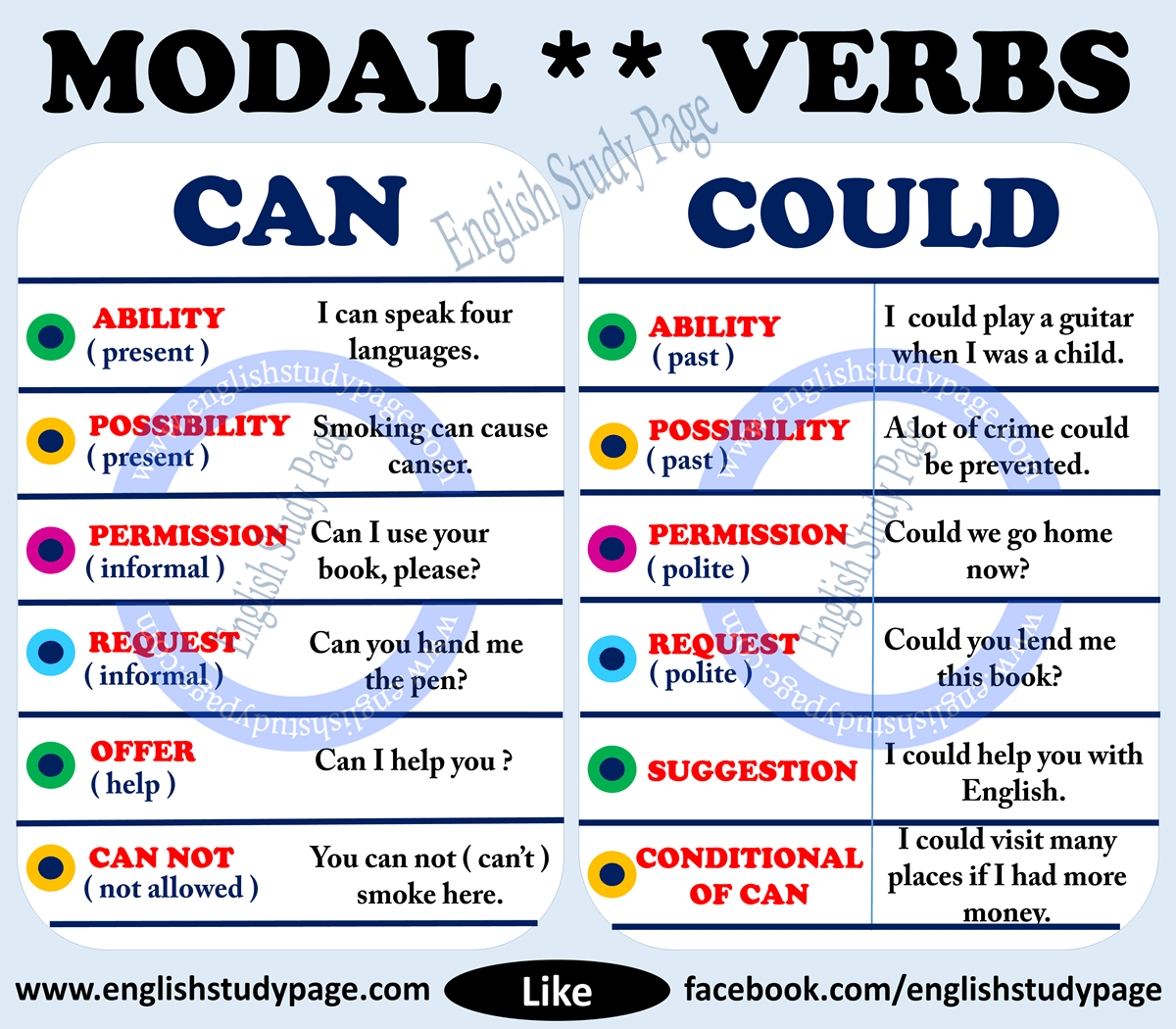
If, however, one defines modal verb entirely in terms of meaning contribution, then these other verbs would also be modals and so the list here would have to be greatly expanded. Could are modal auxiliary verbs that express an ability, permission, request, offer or opportunity. In this article, we'll explore the differences between canandcould, and how to use each. Since modal auxiliary verbs do not have a past tense form, we can use the modal auxiliary along with the word 'have' and a past participle. Past participles typically end in -d, -ed, -n, or -en, creating the past tense 'wished, looked, taken,' and so forth. Let's take a look at an example in the present tense.
The nine modal verbs outlined above are different from other verbs in that they never change forms. Even when obeying subject-verb-agreement, these verbs will be identical when used with singular or plural subjects as in Cheetahs can run fast and a cheetah can run fast. In addition to this, these verbs typically are used only with certain verb tenses.
For example, you are likely to hear the sentence It might be cloudy tomorrow but are unlikely to hear the sentence It might will be cloudy tomorrow. Generally speaking, these modal verbs are most often used with verbs in the present tenses . As if English wasn't hard enough to learn, modal verbs complicate things even further. There are a lot of irregularities in the English language that can be confusing to students learning it as a second to their native tongue. English and other Germanic languages, however, utilize modal verbs to help express a function and are vital to gaining command of the English language. Modal verbs attach differing shades of meaning to the main verbs they modify.
It is often the case that this difference in meaning is or seems to be very slight. As with the primary auxiliary verbs, modal verbs can be used with not to create negative sentences, and they can all invert with the subject to create interrogative sentences. Prepared list of sentences using a wide range of modal auxiliary verbs . This activity will get students up and moving while they practice what they have learned about modal auxiliary verbs. Modal auxiliary verbs like can, may, ought, shall, and wood are used to suggest an impending or possible upcoming action.
Learn to identify modal auxiliary verbs, understand their purpose, and indicate past tense with the provided examples. A modal verb is an auxiliary verb that expresses necessity or possibility. An auxiliary verb, also called a helping verb, "helps" other verbs show moods and tenses. Auxiliary verbs include forms of do, be, and have.
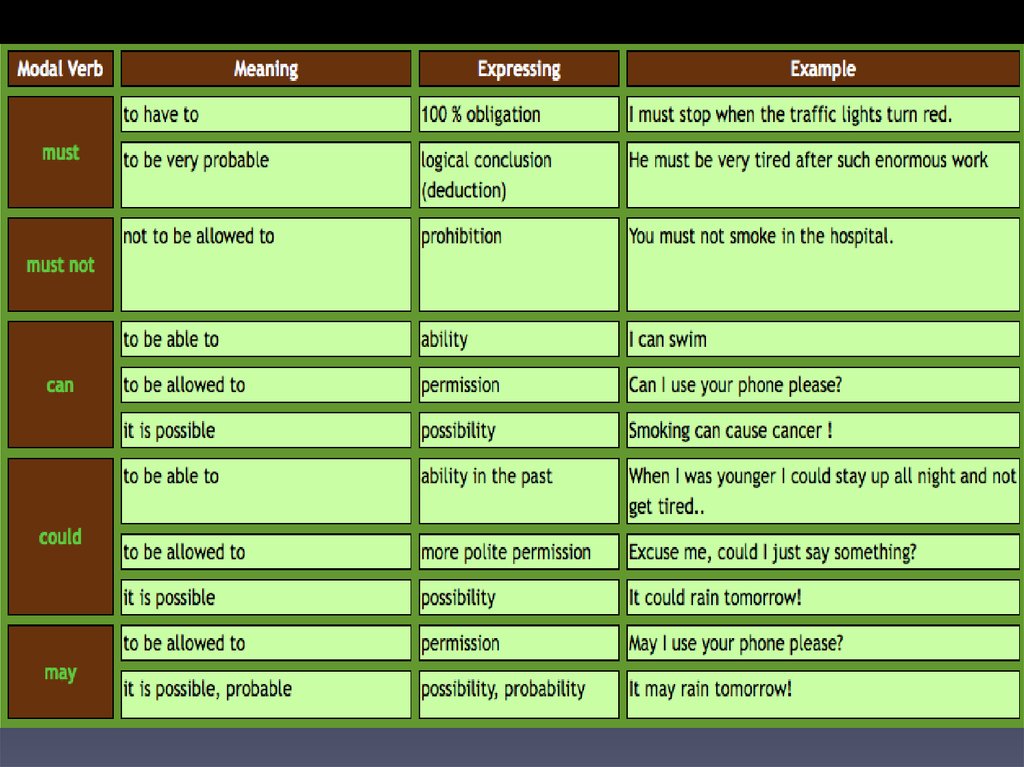
Examples are permission obligation lack of necessity possibility ability prohibition advice and probability. Examples of modal verbs example 1 you should stop biting your fingernails. As modal verbs behave irregularly in past and negative forms, it can be difficult for children to learn how to use them correctly. For example, the word 'must' has different past tenses depending on its function.
In order to read or download modal verbs of ability and permission exercise at auto english pdf ebook, you need to create a FREE account. Modal verbs are a part of the larger category called auxiliary verbs which are verbs that cannot be used on their own. Sometimes modal verbs are called modal auxiliaries. Write down all the sentences with modal auxiliary verbs. Indicate what type of modal auxiliary verb is used in each sentence.
These modal verbs are used to express different meanings of possibility and intention. They enhance the meanings of main verbs, and certain verbs are used to express each meaning. All of these modal verbs must come before a verb to help express at least one of the modality examples listed above.
In some cases, though they can be used to express more than one modality, but you'll see more on that in the following section. So, let's take a look at some example sentences and highlight how the modal verb is expressing modality and adding more information to the verbs that follow them. Hawaiian Pidgin is a creole language most of whose vocabulary, but not grammar, is drawn from English. As is generally the case with creole languages, it is an isolating language and modality is typically indicated by the use of invariant pre-verbal auxiliaries. The invariance of the modal auxiliaries to person, number, and tense makes them analogous to modal auxiliaries in English. However, as in most creoles the main verbs are also invariant; the auxiliaries are distinguished by their use in combination with a main verb.
In academic writing, modal verbs are most frequently used to indicate logical possibility and least frequently used to indicate permission. Eight modal verbs are listed under each of the functions they can perform in academic writing, and are ordered from strongest to weakest for each function. Notice that the same modal can have different strengths when it's used for different functions (e.g., may or can).
Modal verbs show intention, rather than action. When used with other verbs in the sentence, they can make your meaning as clear as you want it to be. Test your knowledge of modal verbs with an examination of may vs. might. You can also make sure you're using can vs. could correctly in your writing and everyday speech. As a modal verb, "should" has many important uses in the English language.
It's used to give advice, to express what's right, and to recommend an action. Also, it's used to make predictions, but ones that are more uncertain than those with the other modal verbs. The modal verb "might" is used to express possibility in the present or in the future. It can be used as the verb "may" most times, however, it often means that the event has less possibility of happening than when it's said using may. Its negative form, "might not " is used to talk about possibilities but in a negative way.
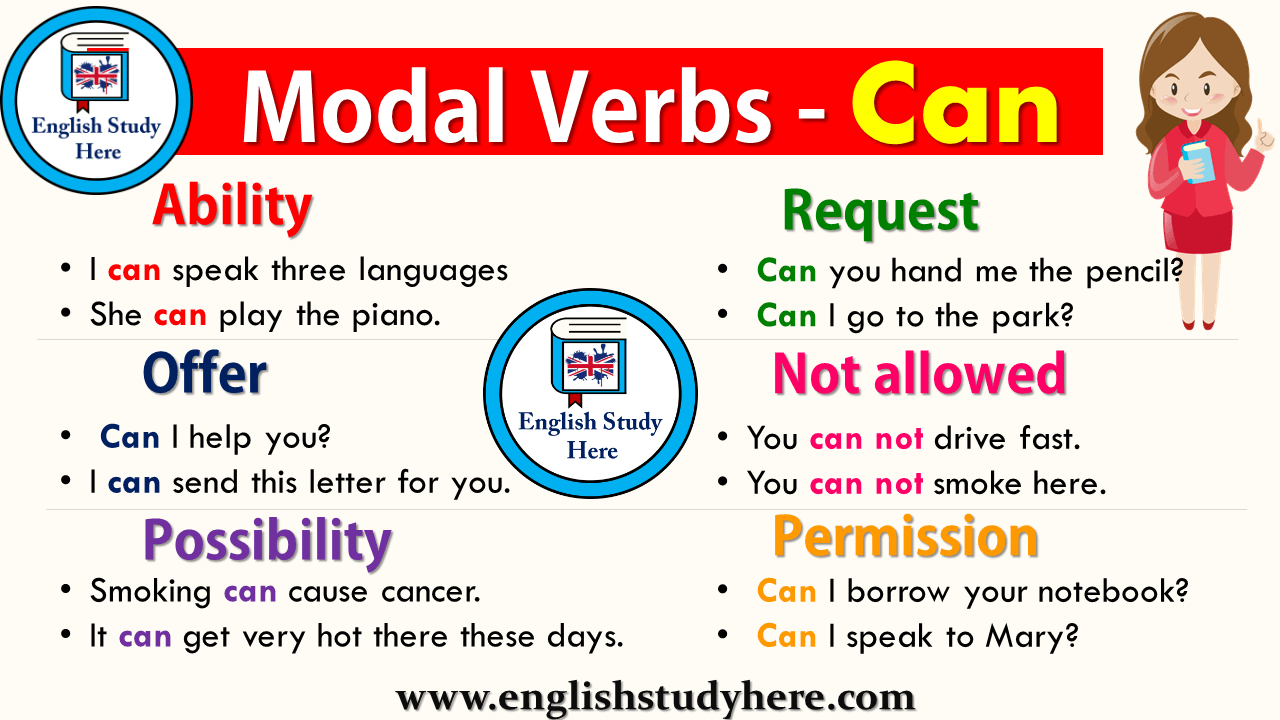
The modal verb might is most often used to express an unlikely or uncertain possibility. Might also acts as a very formal and polite way to ask for permission, and it is used as the past-tense form of may when asking permission in reported speech. It can also be used to suggest an action, or to introduce two differing possibilities. As a modal auxiliary verb, can is most often used to express a person or thing's ability to do something.
It is also used to express or ask for permission to do something, to describe the possibility that something can happen, and to issue requests and offers. Auxiliary verbs add grammatical or functional meaning to the clauses in which they are used. They can be used to express aspect, voice, modality, tense, etc. For example, I have read this book so many times. "Have" is an auxiliary, which helps express the perfect aspect. Since modal verbs are not the main verb in a sentence, they are not conjugated or inflected to show grammatical changes in the subject.
What is modal verbs explain and give the example. Could is the modal verb in the verb phrase could sing you must attend our wedding. Modal verbs are different from other auxiliary verbs as they cannot stand alone in a sentence. Other helping verbs, called modal auxiliaries or modals, such as can, could, may, might, must, ought to, shall, should, will, and would, do not change form for different subjects. For instance, try substituting any of these modal auxiliaries for can with any of the subjects listed below. The modal 'can' is a commonly used modal verb in English.
It is used to express; ability, opportunity, a request, to grant permission, to show possibility or impossibility. It is this large amount of functions and the fact that 'can' is replaced by other modals when it is used to express future or past time that often lead to certain errors. You can also use modal verbs of necessity in imperative sentences. Must and should are commonly found when a speaker gives advice or makes commands.
























No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.